Unlocking the power of your data: A comprehensive master data management framework
Master Data Management (MDM) is a critical aspect of data management for organizations as it ensures that a single, accurate and consistent version of important data elements is available across the enterprise. A master data management framework is a set of guidelines and best practices that organizations use to design and implement their master data management program.
In the blog post, we will answer the following questions:
- Why is a master data management framework needed?
- What could an example of a master data management framework look like?
- How to get from master data management framework to reality?

Why is a master data management framework needed?
The need for a master data management framework arises from the following six factors:
-
Data duplication
Without a master data management framework, data is often duplicated and inconsistent across different systems and data sources, making it difficult to use and trust.
-
Data quality
Without a master data management framework, data can be inaccurate, incomplete, and inconsistent, which can lead to poor decision-making and wasted resources.
-
Data integration
Without a master data management framework, it can be difficult to integrate data from different systems and data sources, which can make it difficult to access and use the data.
-
Data security
Without a master data management framework, data can be vulnerable to security breaches, which can lead to data loss and regulatory compliance issues.
-
Data governance
Without a master data management framework, it can be difficult to implement and enforce data governance policies, such as data quality, data lineage, and data security, which can lead to poor data governance and compliance issues.
-
Data analytics
Without a master data management framework, it can be difficult to gain insights and make business decisions from the data, which can hinder business growth and decision making.
A master data management framework provides a structure and a set of best practices that organizations can use to design and implement their master data management program to ensure that data is accurate, complete, consistent and secure, and that data governance policies are enforced. It also enables organizations to gain insights from their data and make better business decisions.
What could an example of a master data management framework look like?
A master data management framework is a set of guidelines and best practices that organizations use to design and implement their master data management program. The framework provides a structure for creating, maintaining, and governing a single, accurate, and consistent version of important data elements across the enterprise.
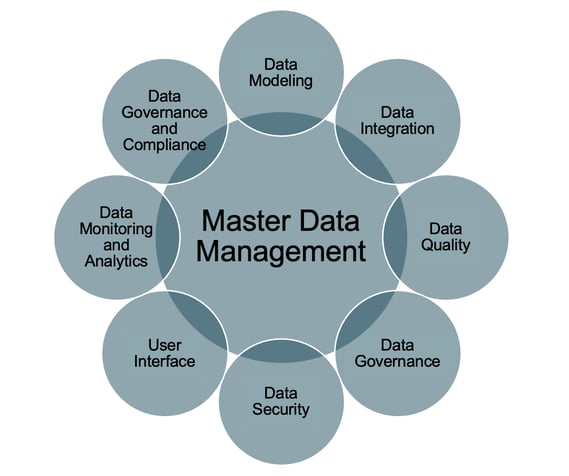
An example of a master data management framework could include the following components:
1. Data governance
This component defines the policies, processes, and governance structures needed to manage master data, including data quality, data lineage, and data security.
2. Data modeling
This component defines the structure and organization of master data, including data entities, data attributes, and data relationships.
3. Data integration
This component defines the processes and tools used to integrate master data with other systems and data sources, such as data warehousing, data lakes, and other data management systems.
4. Data quality
This component defines the processes and tools used to ensure the accuracy, completeness, and consistency of master data, including data profiling, data validation, data matching, and data survivorship.
5. Data security
This component defines the processes and tools used to protect master data, including data encryption, data access controls, and data masking.
6. User interface
This component defines the interfaces and tools used to access and work with master data, including self-service data portals, data visualization, and data management tools.
7. Data monitoring and analytics
This component defines the processes and tools used to monitor and analyze master data, including data lineage visualization, data quality monitoring, and data analytics.
8. Data governance and compliance
This component defines the processes and tools used to comply with regulatory and industry standards, such as data governance, data quality, and data security.
This is just one example of how a master data management framework could look. However, different organizations may have different needs and requirements. Therefore, the framework should of course be tailored to the specific needs of the organization at scope and should be continuously reviewed and updated as necessary.
From master data management framework to reality
Implementing a master data management framework is a multi-step process that involves several key components, including data governance, data quality, data integration, data security, and data management. Here are eight steps that organizations can take to move from a master data management framework to reality:
-
Identify and define master data domains
Identify the important data elements that are critical to the organization's operations and define the master data domains that need to be managed, such as customer, product, and supplier data.
-
Establish data governance
Establish a data governance program to ensure the accuracy, completeness, and consistency of master data, and to enforce data governance policies, such as data quality, data lineage, and data security.
-
Implement data quality processes
Implement data quality processes, such as data profiling, data validation, data matching, and data survivorship, to ensure the accuracy, completeness, and consistency of master data.
-
Integrate master data with other systems
Integrate master data with other systems and data sources, such as data warehousing, data lakes, and other data management systems, to ensure that master data is accessible and usable across the organization.
-
Implement data security measures
Implement data security measures, such as data encryption, data access controls, and data masking, to protect sensitive master data.
-
Provide user access
Provide user access to master data through self-service data portals, data visualization, and data management tools, to ensure that master data is accessible and usable across the organization.
-
Continuously monitor and improve
Continuously monitor and improve the master data management program by regularly assessing the quality, completeness, and consistency of master data and making necessary improvements.
-
Test and deploy
Test the master data management system in a non-production environment, and deploy it to the production environment after testing.
It is important to note that this is a high-level overview of the process and that each organization may have different needs and requirements. It's also important to have a team of experienced professionals in data management and governance, to ensure a successful implementation.
EBOOK
Ready to build your business case for Master Data Management?